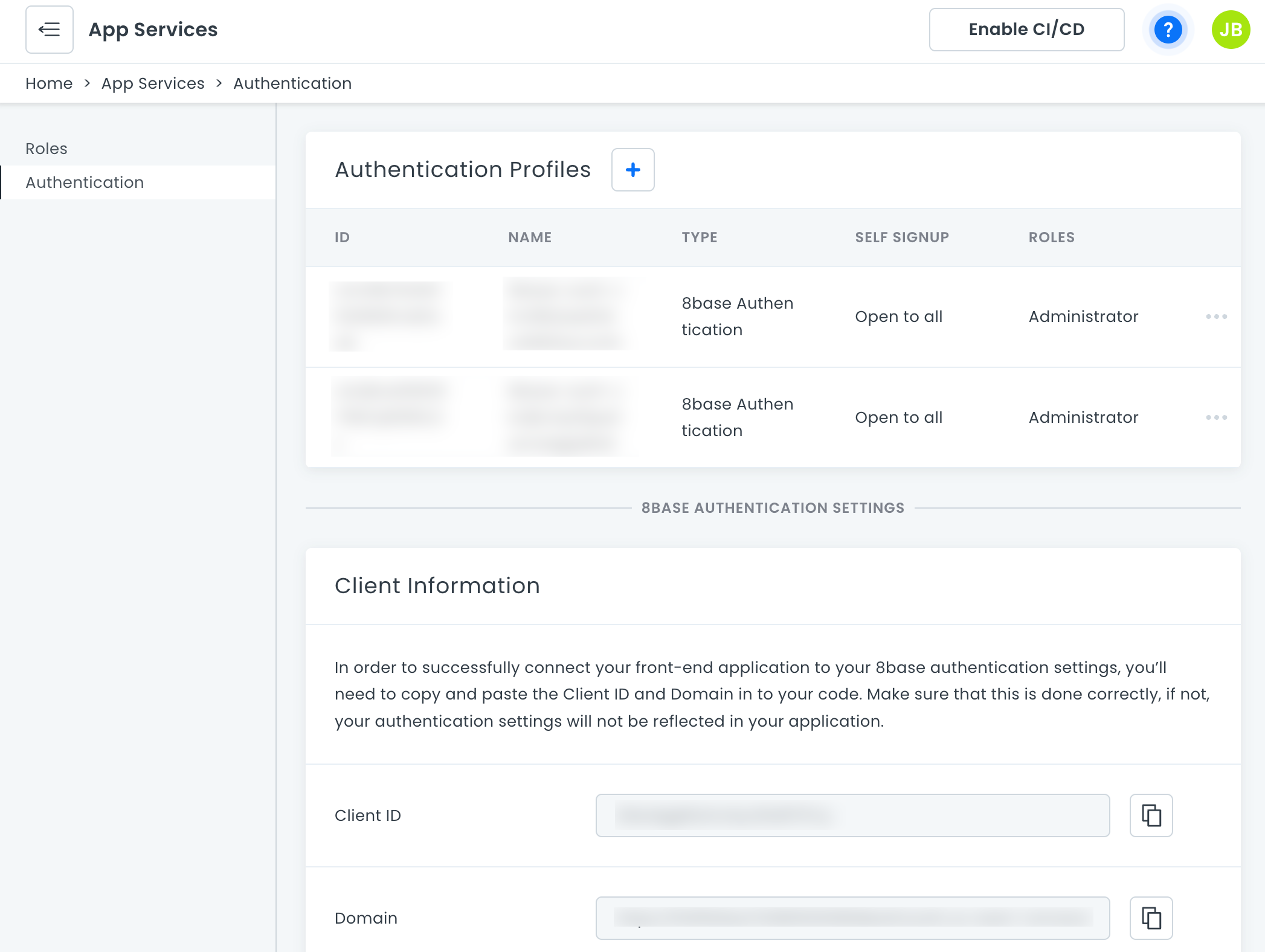
Authentication
8base authentication is the default option for all workspaces. Upgraded workspace plans have the option to connect Auth0 accounts or an OpenID provider.
- 8base Authentication: Running on AWS Cognito, this provides an integrated experience within 8base without additional services.
- Auth0: If you have existing authentication schemes with Auth0, you can integrate it into your 8base backend.
- OpenID: For developers leveraging a compliant service to manage their users' authentication needs.
Login / Signup
8base does not store or manage passwords. All login credentials are stored with an auth provider. This means that only an auth provider can login or register a user! Therefore, 8base allows you to use GraphQL mutations or a Hosted Login Page to send a user's credentials to auth providers. However, it's the auth provider's system that will validate a user's credentials and identity.
Issuance
When an auth provider authenticates a user, it issues an idToken. Think of the idToken as a temporary passport that contains information about the user that authenticated. This idToken get's returned to the front-end application. It can be stored and used to authenticate API requests made to an 8base workspace.
To dive deeper into idTokens (JSON Web Tokens), please visit https://jwt.io/
User Query
Simply authenticating a user doesn't add them to a workspace's Users table in 8base. However, using the idToken, an authenticated request can be sent to the workspace API and check whether the token's user exists. To authenticate that request, the token only needs to be added as a Bearer token in the authorization header.
For example, if you're using JavaScript fetch to handle the request, your script might look something like the following.
fetch('8BASE_WORKSPACE_API_ENDPOINT', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Authorization: `Bearer ${idToken}`,
},
body: JSON.stringify({ query: '{ user { id } }' }),
})
.then(userExistsCallback)
.catch(userDoesntExistCallback);
Verification
When 8base receives an authorized API request (a request containing an idToken) it validates that token with the issuing auth provider. 8base handles this step using data that's encoded in the idToken. This way, a fraudulent token is detected and discarded before any sensitive data is accessed.
Validation
Once the auth provider validates that the idToken – and the user claiming the token – are authentic, it let's 8base know. 8base now can confidently extract the user's primary identifier from the token (for example, email address) and query an existing record in the Users table.
Query Response
If the query runs successfully and a user record is returned, great! Just ensure to continue sending the idToken in the authorization header on future API calls.
If the query fails and a user record is not found, we simply need to create a record for the new user. This can be accomplished using the userSignUpWithToken, as seen below.
mutation {
userSignUpWithToken(
authProfileId: "8BASE_AUTHENTICATION_PROFILE_ID"
/* if not specified - will be executed with the
first auth profile in authenticationProfilesList */
user: {
email: "my@email.co"
// ...any other user data
}
) {
id
}
}
Troubleshooting
'Not Authorized' error
If you're unable to get the authentication provider to work and are receiving a Not Authorized error message, you may need to update the associated role and its API permissions. You can do this by first ensuring that the configured provider has an associated role, like Guest. Next, navigate to App Services > Roles > [ROLE_NAME] > Data and ensure that the role is enabled for the Get Token function call.
Mismatch between auth provider user pool and 8base Users table
Make sure you keep Users table records in 8base up to date with records in your authentication provider user pool. Let's say you are using Custom Auth0 and have manually changed the email for some User record in 8base. This will lead to an authentication error because the email (primary identifier) from the Auth0 token and email from the existing User record are different.