Extending the API
There are situations where the default API does not cover every requirement. Applications may want to have more complex operations, integrations, or additional logic. For that you can add different capabilities to your backend.
For more information about custom functions, see: Custom Functions.
Getting Started
In our case we have a movie database, but we want to be able to get reviews for each movie straight from ChatGPT. For that, we will add an additional resolver. For more information, see: [Resolvers](https://docs.8base.com/backend/custom-functions/custom-functions /resolvers).
First we will generate our local development environment and select our project:
8base init DocsOps
Before we start coding, we need to add axios to interact with the OpenAI API and install the dependencies.
npm install axios --save
npm install
Next we will generate our resolver. The command below gives:
- The skeleton of the resolver
- A file to manage the associated schema
- A default mock file to use for local testing
8base generate resolver movieWithReview -s js
The default project has four examples. You can clean up the file structure and the 8base.yml until only the resolver we need remains.
functions:
movieWithReview:
type: resolver
handler:
code: src/resolvers/movieWithReview/handler.js
schema: src/resolvers/movieWithReview/schema.graphql
Define the Schema
Let's modify the schema (src/resolvers/movieWithReview/schema.graphql) so we can specify what our resolver will receive and return.
We will add a type with the data we want to return:
type MovieWithReviewType {
id: ID,
title: String,
genre: String,
director: String,
rating: String,
review: String
}
Then we can specify what the result will look like:
type MovieWithReviewResult {
result: MovieWithReviewType
}
Lastly, we need the caller to send the id of the movie we want to get the review for. And we will specify that we are returning a MovieWithReviewResult instance.
extend type Query {
movieWithReview(id: ID!!): MovieWithReviewResult
}
Implementing the Handler
Now let's write our resolver in src/resolvers/movieWithReview/handler.js.
We will need to retrieve the data of the movie in question, using the id provided by the parameter. Incoming data can be accessed using the event object. As our data is in 8base, we can use a GraphQL query to get it.
First we define the query:
const GETMOVIE = gql `
query getMoview($id: ID!) {
movie(id: $id) {
id
title
genre
director
rating
}
}
And then we execute it:
const result = await ctx.api.gqlRequest(GETMOVIE, { id: event.data.id })
For the interaction with OpenAI, we will wrap things in a function. OpenAI endpoints require an API key, so we will keep that as an environment variable.
const openAiChatEnpoint = 'https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions';
const openAIKey = process.env.OPENAI;
const chat = async function (movie) {
const data = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": `You are a movie critic. Provide a brief review of the movie ${movie}}`
}
]
}
return axios.post(openAiChatEnpoint, data, {
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${openAIKey}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Accept': 'application/json'
}
});
}
Once we have retrieved the details of the movie, we can call our chat method to get the review from ChatGPT:
const review = await chat(result.movie.title);
From there, we just need to assemble the response to send. Putting it all together, it looks like this:
import gql from 'graphql-tag';
const axios = require('axios').default;
const openAiChatEnpoint = 'https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions';
const openAIKey = process.env.OPENAI;
const chat = async function (movie) {
const data = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": `You are a movie critic. Provide a brief review of the movie ${movie}}`
}
]
}
return axios.post(openAiChatEnpoint, data, {
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${openAIKey}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Accept': 'application/json'
}
});
}
const GETMOVIE = gql `
query getMoview($id: ID!) {
movie(id: $id) {
id
title
genre
director
rating
}
}
`
module.exports = async (event, ctx) => {
const result = await ctx.api.gqlRequest(GETMOVIE, { id: event.data.id })
const review = await chat(result.movie.title);
const returnData = {
id : result.movie.id,
title: result.movie.title,
genre: result.movie.genre,
director: result.movie.director,
rating: result.movie.rating,
review: review.data.choices[0].message.content
}
return {
data: {
result: returnData
},
};
};
Testing and Deploying
We can use mocks to test different scenarios without custom functions. In our case, our mock should look like this:
{
"data": {
"id": "clnnd8hii00ax08i75bw34i58"
}
}
Because we are using an environment variable, we need to set it up before making our local call. There are many ways to accomplish this, but we will set it before calling our method locally.
OPENAI=XXXXXXX 8base invoke-local movieWithReview -p src/resolvers/movieWithReview/mocks/request.json
We will get the following results:
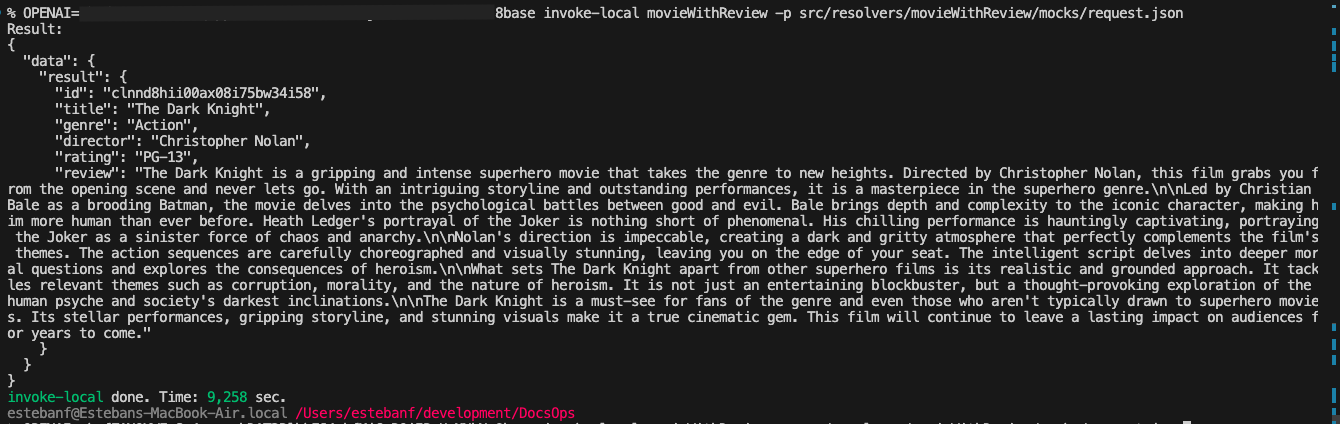
Input this call in order to deploy:
8base deploy
Executing the Custom Resolver
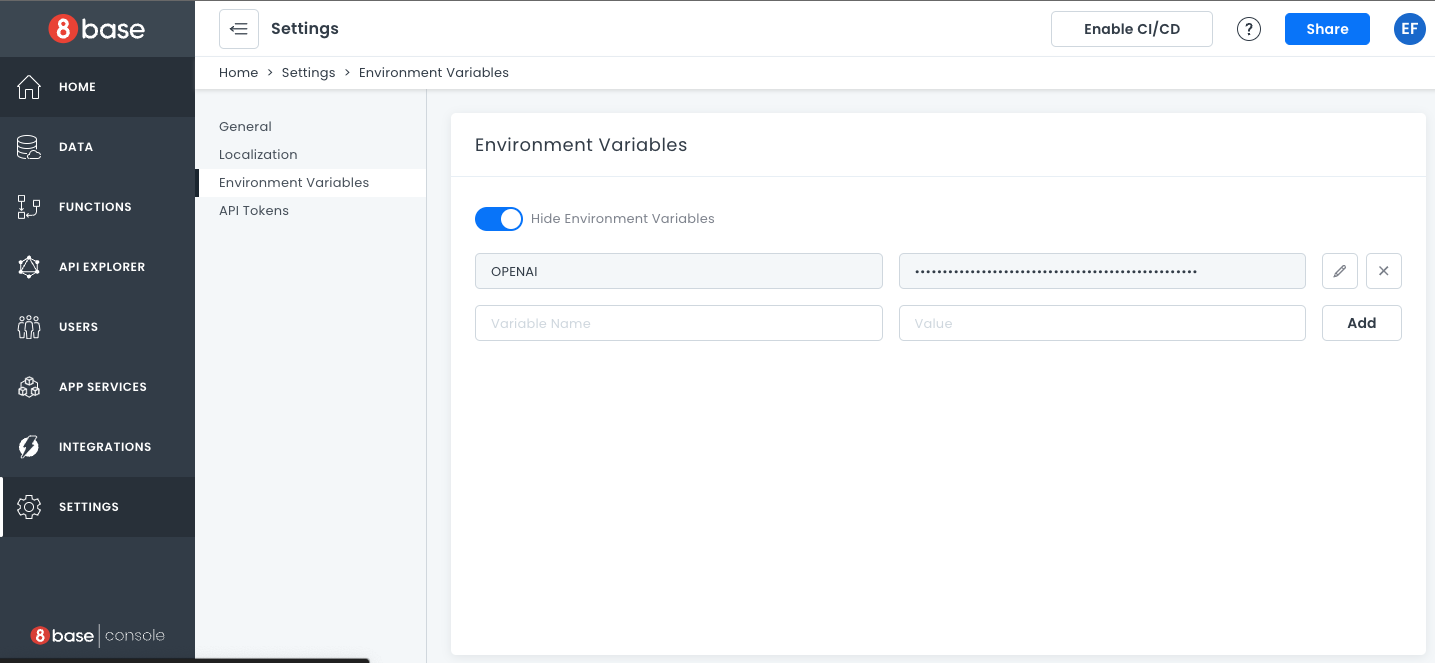
First, we need to set up our environment variable:
- Go to Settings.
- Select Environment Variables.
- Enter the name and then the value of your key. In our case, the name is “OPENAI”.
- Click Add.
Now the environment variable will be available to your custom function.
Then we can execute our query in the API explorer.
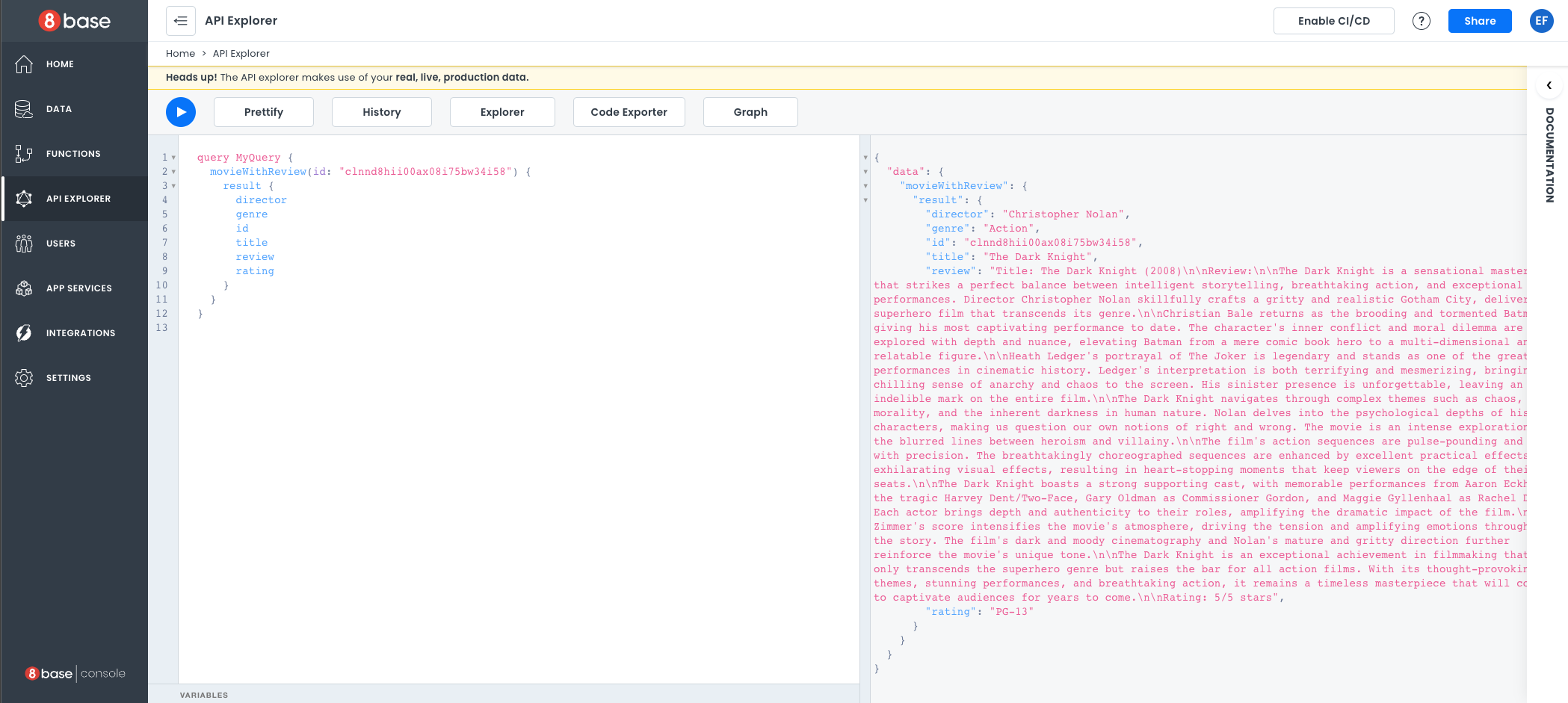
As you can see, our results include a full movie review.