Data Builder
The 8base Data Builder is a data modeling interface for defining database tables, field types, and relationships between tables.
To open the Data Builder, click Data in the sidebar, select the table you want to work on, and then click the Schema tab.
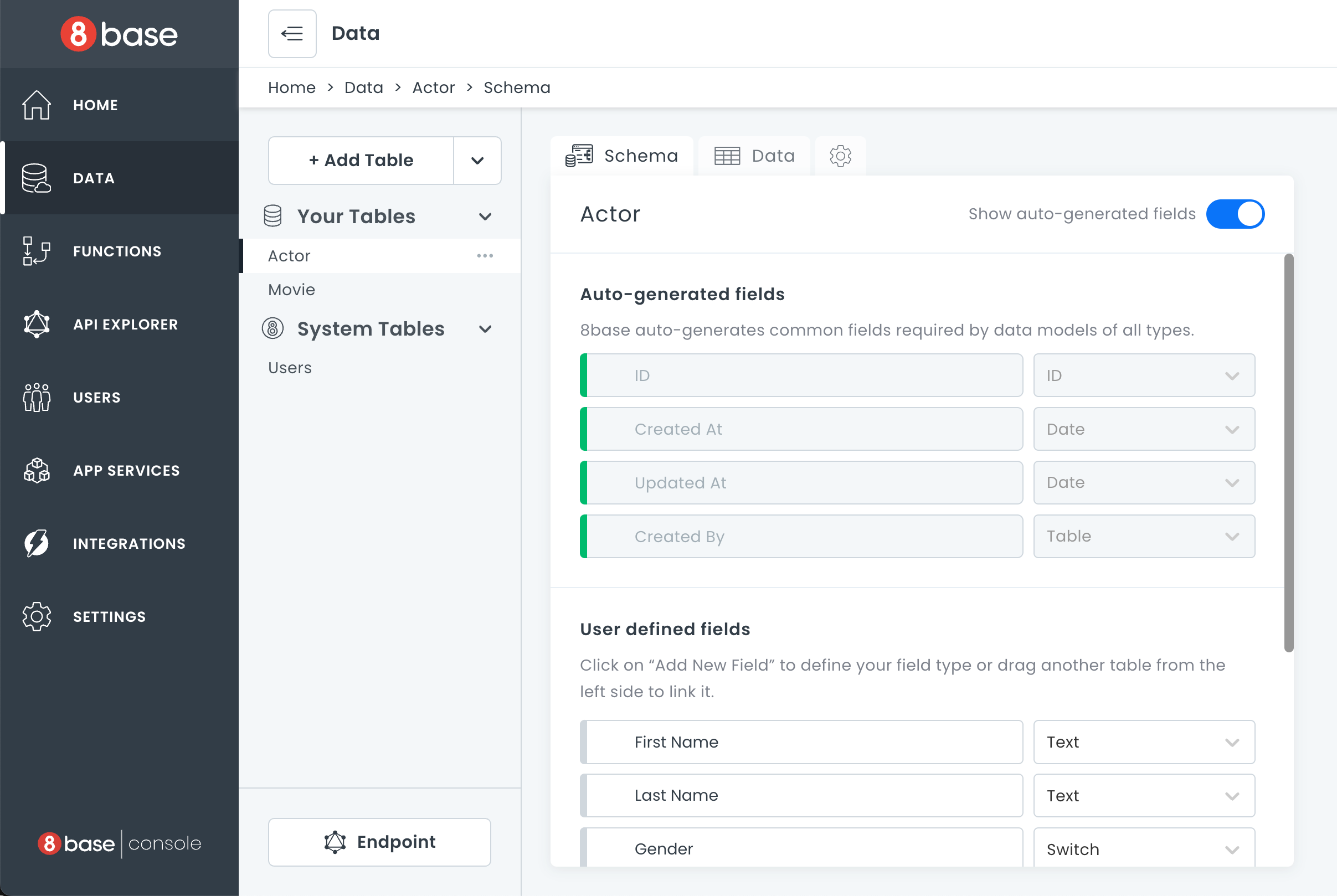
For each table defined, the 8base GraphQL engine creates GraphQL schema object types and the corresponding query, mutation, and subscription fields with resolvers automatically.
This means that all Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) actions, as well as real-time connections (websockets) are immediately available to use via the workspace's unique API endpoint.
Working with Tables
In the background, 8base spins up an Aurora MySQL database instance for your workspace. Aurora is a relational database that can handle complex queries and is ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) compliant. When tables are created, updated, and deleted in a workspace, 8base handles the corresponding migrations and executes them immediately against the database. Therefore, you're database is always reflected by the Data Builder UI - showing all available fields, validations, tables, and relations.
Creating Tables
Click the + Add Table button to create a new table. The default name for new tables is "Untitled Table". All tables require unique names (attribute, workspace names and their plural form are reserved and cannot be used in any letter cases).
As soon as a table is created, corresponding GraphQL schema types and query, mutation, and subscription resolvers will be generated automatically.
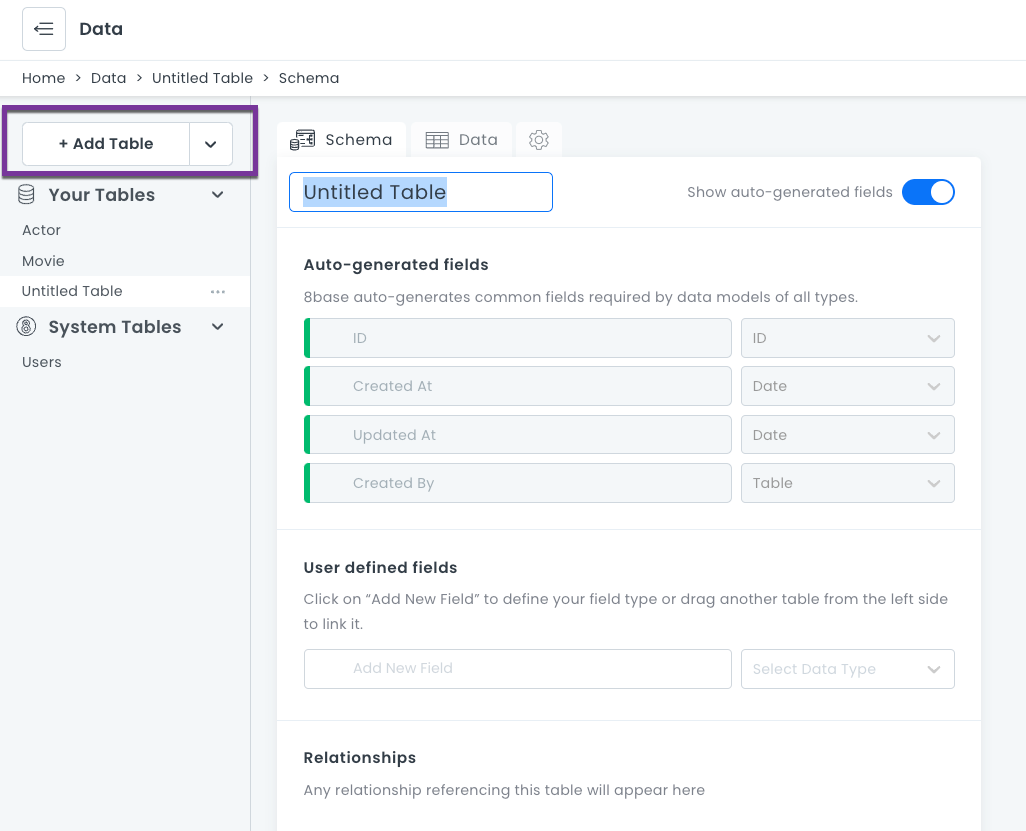
Updating Tables
After a table is created, fields and relations can be defined. All updates to a table are published in real-time, giving a seamless experience between defining a data model and having it be highly available.
As soon as a table is updated, its corresponding GraphQL schema types and query, mutation, and subscription resolvers will be updated automatically.
To ensure that table related errors and mistakes are minimized, 8base protects against many harmful actions. Some of these include:
- A prompt that requires a Default Value will appear when changing a non-mandatory field to mandatory.
- Date, Number, and Text field values are automatically converted when an existing field type is updated.
- When changing a non-unique field to unique, current records are validated for having unique values.
Deleting Tables
To delete a table:
- Go to the table name and click ....
- Click Delete.
- A confirmation dialog opens. Type in the table name and click Delete.danger
Deleted tables cannot be restored and any existing table records will be lost. Additionally, if there are tables that are related to the table being deleted - belongs to and has many, either specified as mandatory or not - those relations will be severed.
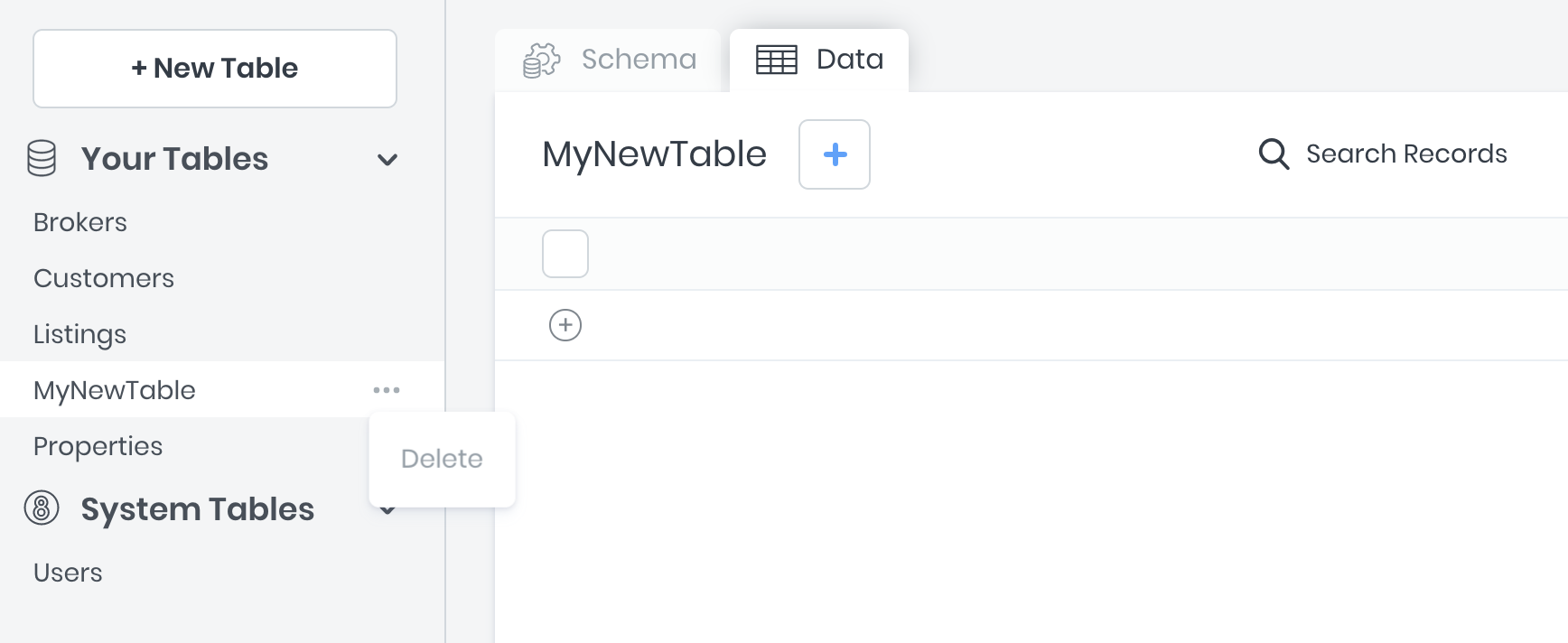
Table Relationships
8base supports three types of table relationships to be defined that are congruent with what to expect from relational databases:
| Type | A to B | B to A |
|---|---|---|
one-to-one | Records in table A may have_one or belong_to records in table B. | Records in table B may have_one or belong_to records in table A. |
one-to-many | Record in table A may have_many records in table B. | Records in table B may have_one or belong_to records in table A. |
many-to-many | Record in table A may have_many records in table B. | Record in table B may have_many records in table A. |
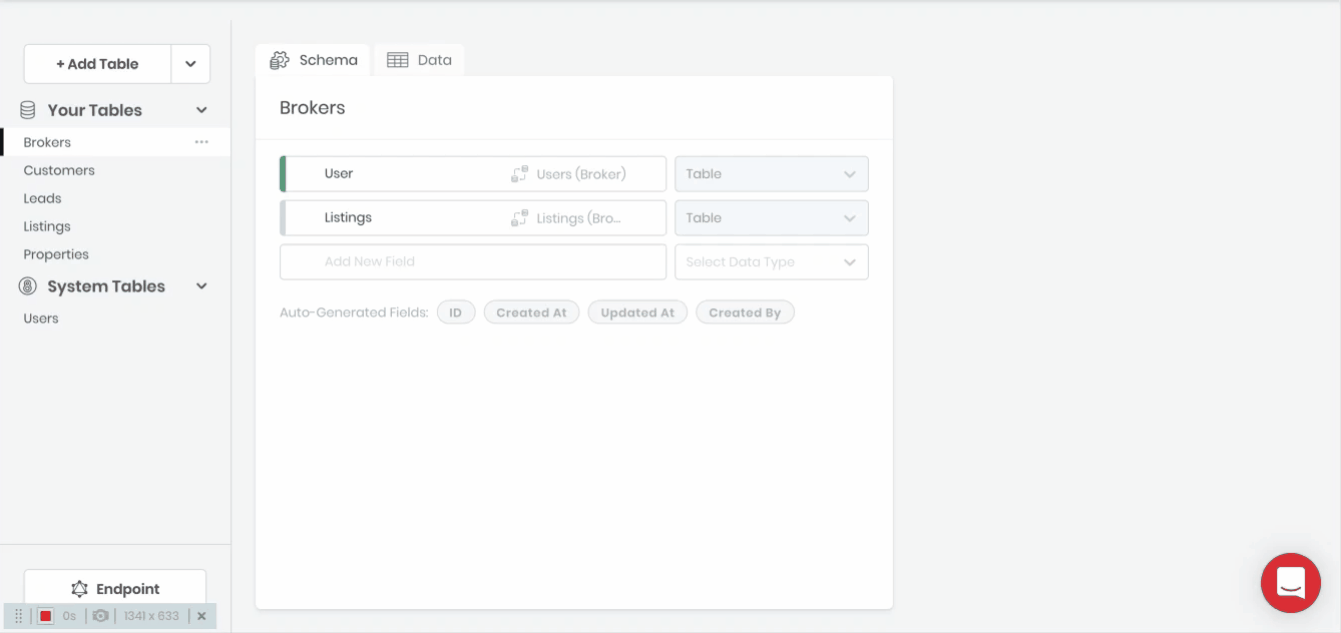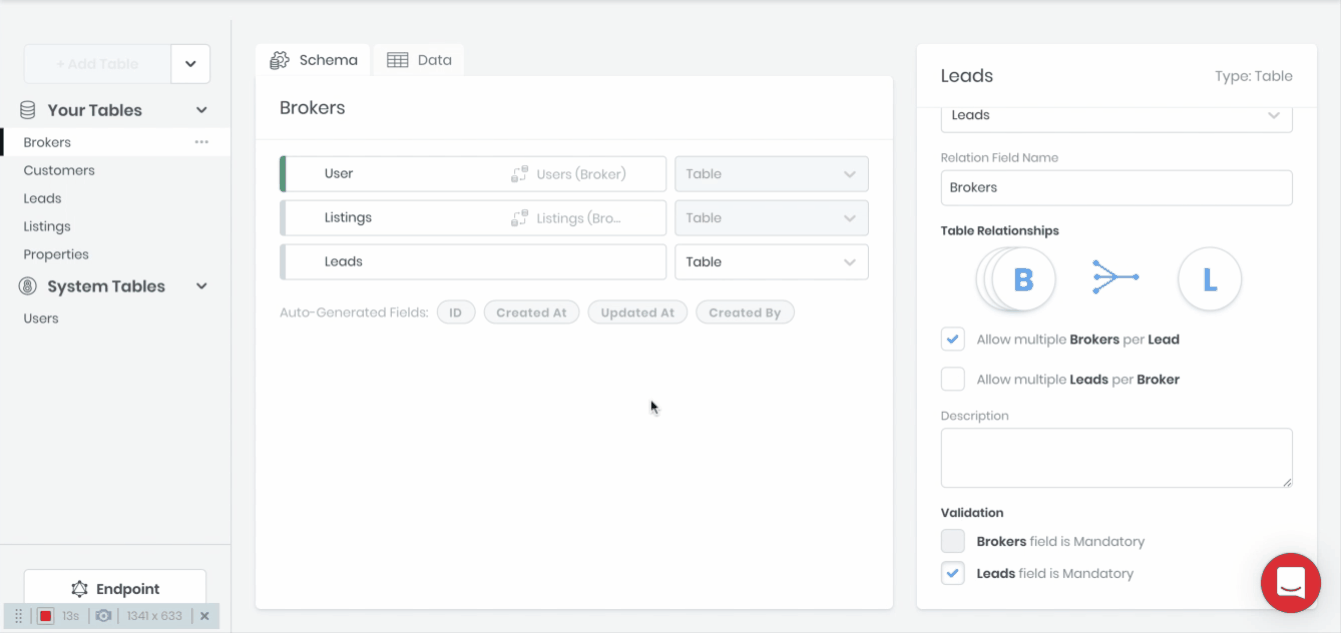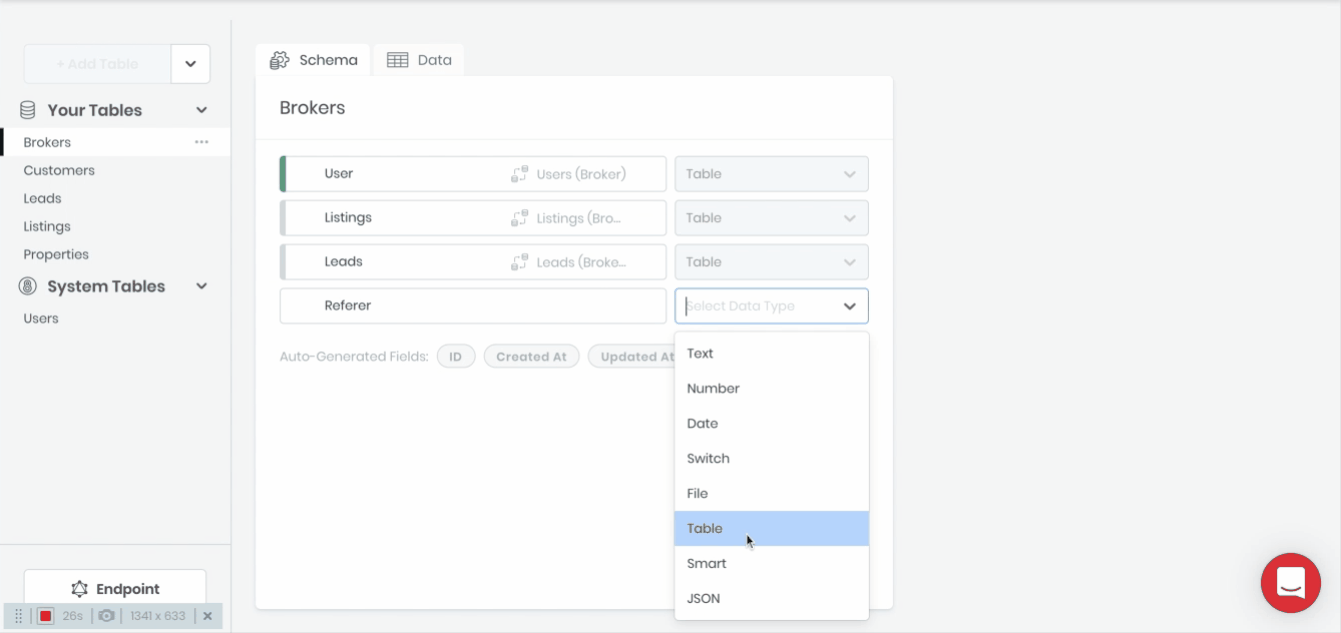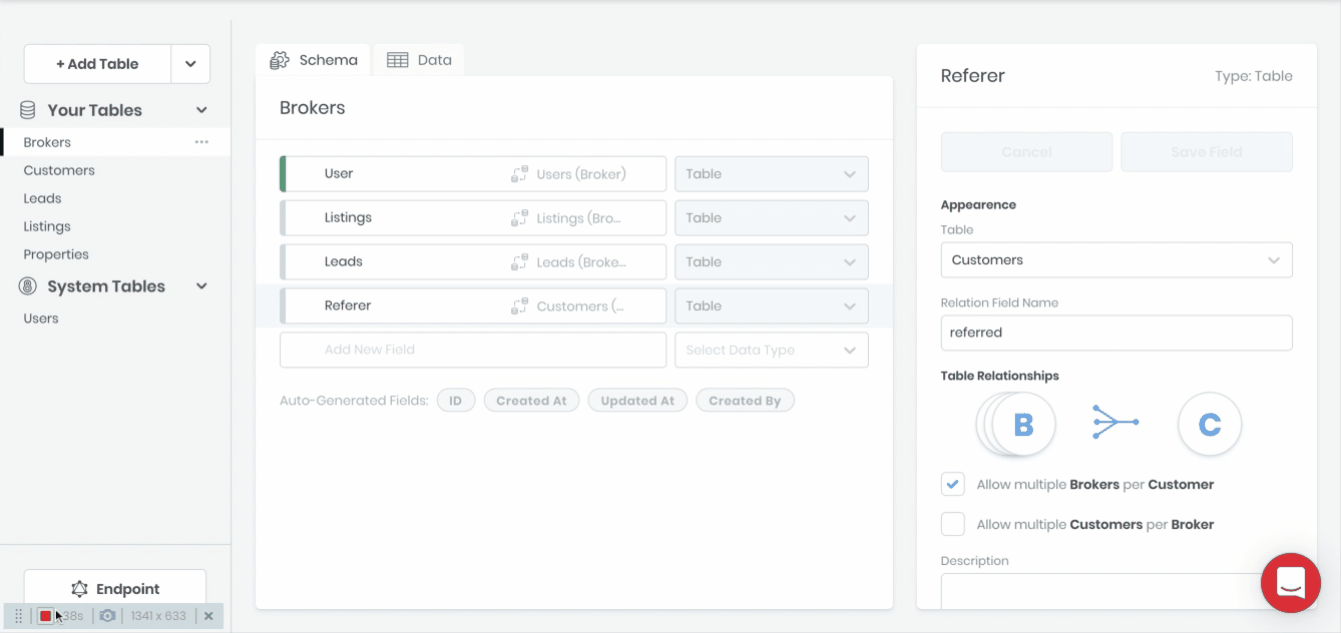
Defining a relationship between two tables can be accomplished by dragging and dropping one table onto another or by selecting Table as the Data Type when creating a new table field.
Table Configurations
For specifying has many, has one and belongs to relationships between tables.
Configurations
- Table: For selecting what table is to be related.
- Relation Field Name: The name of the relation as it appears on the corresponding table.
- Allow Multiple X to Y: Whether the relationship is has one or has many.
- Mandatory: Whether the field relationship is required.
- Description: An optional text box where you can write information about the field.
Self-Referential Relationships
Self-Referential relationships can be defined by relating tables to themselves! For example, a the Users table might have a many-to-many relationship with itself, and use a named association of friends.
Table Types
There are three table types: Custom, System, and View.
Custom Tables
Custom tables are the tables created in any workspace by an administrator. They are fully customizable.
System Tables
System tables are tables that come automatically with a workspace. For example, the Users table. They are fully extensible, meaning that new fields and relations can be added to them. However, these tables cannot be deleted or renamed. Their default fields cannot be changed.
View Tables
View Tables are virtual tables that aggregate fields from several tables into a single view. Under the hood, they are based on the result-set of an SQL statement. In a workspace, they can be created using the viewCreate GraphQL mutation in the API Explorer.
For more information on views, see SQL Views.
Salesforce data can be imported as View Tables. For more information, see Salesforce.